Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of mesothelioma can be suspected with imaging but is confirmed with biopsy. It must be clinically and histologically differentiated from other pleural and pulmonary malignancies, including reactive pleural disease, primary lung carcinoma, pleural metastases of other cancers, and other primary pleural cancers.[5] Primary pericardial mesothelioma is often diagnosed after it has metastasized to lymph nodes or the lungs.[4]
Imaging[edit]
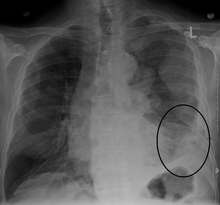
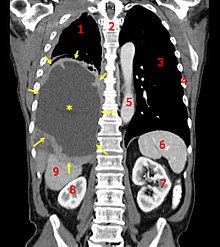
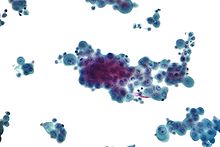
Diagnosing mesothelioma is often difficult because the symptoms are similar to those of a number of other conditions. Diagnosis begins with a review of the patient's medical history. A history of exposure to asbestos may increase clinical suspicion for mesothelioma. A physical examination is performed, followed by chest X-ray and often lung function tests. The X-ray may reveal pleural thickening commonly seen after asbestos exposure and increases suspicion of mesothelioma.[14] A CT (or CAT) scan or an MRI is usually performed. If a large amount of fluid is present, abnormal cells may be detected by cytopathology if this fluid is aspirated with a syringe.[4] For pleural fluid, this is done by thoracentesis or tube thoracostomy (chest tube); for ascites, with paracentesis or ascitic drain; and for pericardial effusion with pericardiocentesis. While absence of malignant cells on cytology does not completely exclude mesothelioma, it makes it much more unlikely, especially if an alternative diagnosis can be made (e.g. tuberculosis, heart failure).[citation needed] However, with primary pericardial mesothelioma, pericardial fluid may not contain malignant cells and a tissue biopsy is more useful in diagnosis.[4]Using conventional cytology diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma is difficult, but immunohistochemistry has greatly enhanced the accuracy of cytology.[citation needed]
Biopsy[edit]
Generally, a biopsy is needed to confirm a diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma. A doctor removes a sample of tissue for examination under a microscope by a pathologist. A biopsy may be done in different ways, depending on where the abnormal area is located. If the cancer is in the chest, the doctor may perform a thoracoscopy. In this procedure, the doctor makes a small cut through the chest wall and puts a thin, lighted tube called a thoracoscope into the chest between two ribs. Thoracoscopy allows the doctor to look inside the chest and obtain tissue samples. Alternatively, the chest surgeon might directly open the chest (thoracotomy). If the cancer is in the abdomen, the doctor may perform a laparoscopy. To obtain tissue for examination, the doctor makes a small incision in the abdomen and inserts a special instrument into the abdominal cavity. If these procedures do not yield enough tissue, an open surgical procedure may be necessary.[citation needed]
Immunochemistry[edit]
Immunohistochemical studies play an important role for the pathologist in differentiating malignant mesothelioma from neoplastic mimics, such as breast or lung cancer that has metastasized to the pleura. There are numerous tests and panels available, but no single test is perfect for distinguishing mesothelioma from carcinoma or even benign versus malignant. The positive markers indicate that mesothelioma is present; if other markers are positive it may indicate another type of cancer, such as breast or lung adenocarcinoma. Calretinin is a particularly important marker in distinguishing mesothelioma from metastatic breast or lung cancer.[5]

Good day to all am Valeria Miguel Ángel From USA..Texas am so happy sharing this great testimony on here, I was diagnose of Stage IV colon cancer.i was checking for solution in the internet then miraculously i came Across Dr Itua the powerful herbalist that Cure Numerous Diseases such as-Thyroid Cancer,Uterine cancer,Fibroid,Angiopathy, Ataxia,Arthritis,Amyotrophic Lateral Scoliosis,Brain Tumor,Fibromyalgia,Fluoroquinolone ToxicityBladder cancer,Brain cancer,Hiv,Herpes,Esophageal cancer,Gallbladder cancer,Gestational trophoblastic disease,Head and neck cancer,Hodgkin lymphoma
ReplyDeleteIntestinal cancer,Kidney cancer,Hpv,Lung cancer,Melanoma,Mesothelioma,Multiple myeloma,Neuroendocrine tumors
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma,Oral cancer,Ovarian cancer,Sinus cancer,Hepatitis A,B/C,Skin cancer,Soft tissue sarcoma,Pancreative Cancer,Spinal cancer,Stomach cancer,Vaginal cancer,Vulvar cancer,
Testicular cancer,Tach Diseases,Leukemia,Liver cancer,Throat cancer,
Syndrome Fibrodysplasia Ossificans ProgresSclerosis,Alzheimer's disease,Chronic Diarrhea,Copd,Parkinson,Als,Adrenocortical carcinoma Infectious mononucleosis. ,so I contacted him base on the testimonies I?m seeing about him on the internet, I was cured too by him, kindly contact him today through his email he can help you..drituaherbalcenter@gmail.com and his herbal medicines will set you free from any human diseases,all thank to you Dr Itua for your kindly help in my life his Mobile number Whatsapp.+2348149277967